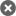Tratat de Pictura / The Art of Painting-Gerard de Lairesse / Londra, 1783
-
Produs:Second Hand, Fără garanție
-
Numar articol:127298243
-
Disponibilitate:Indisponibil
-
Preț:
3.000,00 €1.000,00 € -
Anuntul a expirat la:15.02.2022, 07:23
-
Ai o nelamurire?
-
Vandut de:
-
Vinde si tu:Pune in vanzare un produs ca acesta
-
Optiuni:
Descriere
Vânzatorul este direct răspunzator pentru produsul afișat în această pagină.
Disponibilitate: Indisponibil - Vezi produse similare
Specificatii
Gerard de Lairesse - The Art of Painting in all its Branches Methodically Demonstrated by Discourses and Plates
Editata la Londra, in 1783
Format mare, peste 500 de pagini, Coperti originale lemn si piele integral, Raritate Extrema





Gerard or Gérard de Lairesse (11 September 1640 or 1641 – June 1711) was a Dutch Golden Age painter and art theorist.
Lairesse was born in Liège and was the second son of painter Renier de Lairesse (1597-1667). His broad range of talent included music, poetry, and the theatre. He was perhaps the most celebrated Dutch painter in the period following the death ofRembrandt. His treatises on painting and drawing, Grondlegginge der teekenkonst (1701) and Groot Schilderboek (1707), were highly influential on 18th-Century painters like Jacob de Wit.[2] Students of De Lairesse included the painter Jan van Mieris. He died in Amsterdam.
Gerard or Gérard de Lairesse (11 September 1640 or 1641 – June 1711) was a Dutch Golden Age painter and art theorist.
Lairesse was born in Liège and was the second son of painter Renier de Lairesse (1597-1667). His broad range of talent included music, poetry, and the theatre. He was perhaps the most celebrated Dutch painter in the period following the death ofRembrandt.[1] His treatises on painting and drawing, Grondlegginge der teekenkonst (1701) and Groot Schilderboek (1707), were highly influential on 18th-Century painters like Jacob de Wit.[2] Students of De Lairesse included the painter Jan van Mieris. He died in Amsterdam.
Well-known paintings by de Lairesse include his Allegory of the Five Senses (1668), Diana and Endymion (ca. 1680) and Cleopatra Landing at Tarsus. Some of his paintings show influence by the Iconologia of Cesare Ripa. A versatile artist, De Lairesse also made many prints for book illustrations and painted sets for theatre productions
Among other things, De Lairesse produced:
- A set of illustrations for Govert Bidloo's anatomical atlas Anatomia Humani Corporis (1685).
- A set of illustrations for Gerard Reynst's collection Signorum Veterum Icones (1670), a series of prints based on the Italian statuary in Reynst's Amsterdam collection.
- Painted doors of the organ in the Westerkerk church in Amsterdam.
- Set designs for the Amsterdam theatre.
- A portrait of the Dutch stadholder and king of England, William III of England.
- 105 illustrations in: Godefridi Bidloo, Medicinae Doctoris & Chirurgi, Anatomia Hvmani Corporis: Centum & quinque Tabvlis Per artificiosiss. G. De Lairesse ad vivum delineatis, Demonstrata, Veterum Recentiorumque Inventis explicata plurimisque, hactenus non detectis, Illvstrata[3] Amsterdam 1685
Painting career


Gerard de Lairesse studied art under Bertholet Flemalle and his father Renier Lairesse.[5] In 1664 De Lairesse was forced to flee Liège after a love affair gone wrong. He moved north to Utrecht in the Dutch Republic. When his talent was discovered by art dealer Gerrit van Uylenburgh, he in 1667 relocated to Amsterdam.
At first, De Lairesse was highly influenced by Rembrandt, but later he focused on a more French-oriented style similar to Nicolas Poussin. The French even nicknamed him the "Dutch Poussin".
In Amsterdam during the second half of the 17th Century, the pious austerity and embarrassment of riches of the Protestant Dutch in Rembrandt's age had given way to unbridled opulence, even decadence, and de Lairesse's classical French, or Baroque, style fitted this age perfectly. It made him one of, if not the most popular painter in Amsterdam. De Lairesse was therefore frequently hired to adorn the interiors of government buildings and homes of wealthy Amsterdam businessmen with lavish trompe l'oeil ceiling and wall paintings. Many of these paintings still exist in the original buildings where they were painted, but many owners took the paintings with them when they moved.
For instance, he produced three ceiling paintings in 1671 for the Amsterdam regent Andries de Graeff. The paintings glorified the De Graeff family's role as the protector of the Dutch republic and the works of art can be viewed as a visual statement opposing the return of the House of Orange asStadtholders of the republic. They were created for Andries de Graeffs ‘Sael’ at his mayor’s residence in Amsterdam. The ceiling paintings now adorn the Ferdinand Bol room at the Peace Palace in The Hague.[6]
De Lairesse as art theorist [edit]
His treatises on painting and drawing, Grondlegginge der teekenkonst (1701) and Het groot schilderboeck (1707), were highly influential on later painters like Jacob de Wit. He also worked with many established artists of his day on larger commissions for house decorations, and publications.
He attracted many pupils, including Jan van Mieris, Simon van der Does, and the brothers Teodor and Krzysztof Lubieniecki. According to Houbraken, Jan Hoogsaat was one of his best pupils.[9]According to the RKD his pupils were Jacob van der Does (the Younger), Louis Fabritius Dubourg, Gilliam van der Gouwen, Zacharias Webber (the Younger).[10]
Celebrated during his lifetime and well into the 18th century, he was berated during the 19th century. With or without justification, he was considered superficial and effete, and was held in large part responsible for the decline in Dutch painting. Two hundred years after his death in 1711 the Encyclopædia Britannica, 11th Edition (1911) gave no listing at all for De Lairesse, while devoting four pages of solid text to Rembrandt.[7]
Works by De Lairesse are now on display at many museums around the world, including the Rijksmuseum and Amsterdams Historisch Museum in Amsterdam, the Louvre in Paris, theMetropolitan Museum of Art in New York City, the National Gallery of Art in Washington, D.C., the National Portrait Gallery and Tate Gallery in London, and the Cleveland Museum of Art.
In the Binnenhof (now the seat of the Dutch parliament) in The Hague, a hall which he decorated in 1688 is named after him. A street in Amsterdam, the De Lairessestraat, is also named after
Modalitati de livrare si plata
LIVRARE
PLATA
Politica de retur
- - Produsul nu se poate returna.