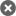PLIANT / POSTER RECLAMA- RENAULT MAJOR
-
Produs:Second Hand, Fără garanție
-
Numar articol:197216708
-
Disponibilitate:Indisponibil
-
Preț:68,00 Lei
-
Anuntul a expirat la:25.10.2023, 11:40
-
Ai o nelamurire?
-
Vandut de:
-
Vinde si tu:Pune in vanzare un produs ca acesta
-
Optiuni:
Descriere
Vânzatorul este direct răspunzator pentru produsul afișat în această pagină.
Disponibilitate: Indisponibil - Vezi produse similare
Specificatii
STARE - NECESITA FOARTE USOARA RECONDITIONARE LA COLTUL PLIULUI.
EXTENSIBIL
PLIANT RECLAMA, CE SE POATE TRANSPORMA IN AFIS.
AN- CCA 1970
FORMAT EXTINS :69 * 62 CM
Renault 8 and 10
| Renault 8 / Renault 10 | |
|---|---|

Renault 8
|
|
| Overview | |
| Manufacturer | Renault |
| Also called | Renault 10 Dacia 1100 Bulgarrenault 8/10 |
| Production | 1962–1973 (Renault 8) 1965–1971 (Renault 10) 1965–1976 (Spain, Renault 8) 1966–1970 (Bulgaria, Bulgarrenault) 1968–1971 (Romania, Dacia) |
| Assembly | Flins, France Mariara, Venezuela Plovdiv, Bulgaria Valladolid, Spain Mioveni, Romania Ciudad Sahagún, Mexico Heidelberg, Australia Casablanca, Morocco[1] St. Bruno, Quebec, Canada Algiers, Algeria (CARAL), Thames, New Zealand (Campbell Industries) |
| Body and chassis | |
| Class | Small family car (C-segment) |
| Body style | 4-door saloon |
| Layout | Rear-engine, rear-wheel-drive |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | Renault 956 cc I4 1100 cc I4 1255 cc I4 1289 cc I4 |
| Transmission | 3-speed manual 4-speed manual 5-speed manual |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | 2,270 mm (89.4 in)[2] |
| Length | 4,000 mm (157.5 in) (Renault 8) 4,200 mm (165.4 in) (Renault 10)[3] |
| Width | 1,490 mm (58.7 in) |
| Height | 1,375 mm (54.1 in)[3] |
| Chronology | |
| Predecessor | Renault Dauphine |
| Successor | Renault 12 |
The Renault 8 (Renault R8 until 1964) and Renault 10 are two rear-engined, rear-wheel drive small family cars produced by the French manufacturer Renault in the 1960s and early 1970s.
The 8 was launched in 1962, and the 10, a more upmarket version of the 8, was launched in 1965. The Renault 8 ceased production and sales in France in 1973. By then the Renault 10 had already been replaced, two years earlier, by the front wheel drive Renault 12.
They were produced in Bulgaria until 1970 (see Bulgarrenault), and an adapted version of the Renault 8 continued to be produced in Spain until 1976. In Romania, a version of the 8 was produced under license between 1968 and 1971 as the Dacia 1100. In total 37,546 Dacia 1100s were built.[4]
Renault 8[edit]
Launch[edit]
The R8 (model R1130) was released in June 1962[2] and was based on the Renault Dauphine with which it shared its basic architecture and its 2,270 mm (89.4 in) wheelbase. The style, closely following that of the first prototype produced, at unusually short notice, by Philippe Charbonneaux, was fashionably boxy; however,[2] while the Renault 8 was actually 30 mm (1.2 in) narrower than the Dauphine, the manufacturer was able to install thick cushioned front seats that were actually each 60 mm (2.4 in) wider, at 560 mm (22.0 in), than those fitted in the Dauphine.[2] The R8's engine followed the pioneering example of the recently introduced Renault 4 by incorporating a sealed for life cooling system.[2] A distinctive innovation on the French produced cars was the fitting of four-wheel disc brakes, a first for a saloon car of this size.[2] However, when in 1965 Renault's Spanish affiliate[5]introduced their own version of the Renault 8 for the (then tariff-shielded) Spanish market, it came with drum brakes.
The 8 was powered by an all new 956 cc Cléon-Fonte engine developing 44 PS (32 kW; 43 hp).
Automatic transmission[edit]
For 1963 (initially only in France), Renault offered an automatic transmission of unique design, developed and produced by Jaeger.[6] It was first shown at the September 1962 Paris Motor Show.[7] Although it was described as a form of automatic transmission at the time, in retrospect it was more realistically a form of automatic clutch, inspired by the German Saxomat device which appeared as an option on several mainstream German cars in the 1950s and 60s.
The clutch in the system was replaced by a powder ferromagnetic coupler, developed from a Smiths design.[7] The transmission itself was a three-speed mechanical unit similar to that of the Dauphine, but from the beginning with synchromesh on all gears in this version.
The system used a dash-mounted push button control panel where the driver could select forward or reverse and a governor that sensed vehicle speed and throttle position.
A "relay case" containing electromagnetic switches received signals from the governor and push buttons and then controlled a coupler, a decelerator to close the throttle during gear changes, and a solenoid to select operation of the reverse-first or second-third shift rail, using a reversible electric motor to engage the gears. The system was thus entirely electromechanical, without hydraulics, pneumatics or electronics.
Benefits included comparable fuel economy to the manual transmission version, and easy adaptability to the car. Drawbacks included performance loss (with only three available gears) and a somewhat jerky operation during gear changes.
The transmission was also used in the Dauphine and the Caravelle.
Engine upgrades[edit]
A more powerful model, the 8 Major (model R1132), was released in 1964, featuring an 1108 cc engine developing 50 PS (37 kW; 49 hp). A still more powerful version, the 8 model R1134 Gordini, was also released that year, with a tuned engine of the same capacity but developing 90 PS (66 kW; 89 hp). The extra power was obtained by a cross-flow head and twin dual-choke 40mm side-draft Solex carburetors. A four-speed close ratio manual transmission, dual rear shock absorbers and uprated springs were fitted. The R1134 Gordini was originally available only in blue, with two stick-on white stripes. It was also distinguishable from the 8 Major by the bigger 200mm headlamp units. In 1965, the Renault 10 Major, a more luxurious version of the 8 with different front and rear styling, was released, replacing the 8 Major.
Facelift[edit]
In 1967, the R8 Gordini (model R1135) received a facelift including two additional headlights (in effect Cibie Oscar driving lights), and its engine upgraded to a 1255cc unit rated at 100 PS (74 kW; 99 hp). The R1134 Gordini cross-flow head design was retained, and twin dual-choke 40mm Weber side-draft carburetors. Both the 8 and the 10 were heavily revised for 1969. Some of the 10's features being incorporated in the 8, resulting in a new 8 Major which replaced the basic model. The changes also saw the addition of the 8S, a sportier model with a 1108cc engine rated at 60 PS (44 kW; 59 hp). 8S model also had the same twin headlights as the R1135 Gordini - the middle ones were for high beam only. The car was delivered with black "RENAULT 8S" tapes, intended for the rear wings but their fixing was left to the customer. Also, the Romanian sport version was named Dacia 1100 S.[8][9]
Modalitati de livrare si plata
LIVRARE
In Bucuresti
-
- Predare personala in max. 7 zile lucratoare
PLATA
- - La predare
- - Ramburs
Politica de retur
- - Produsul nu se poate returna.